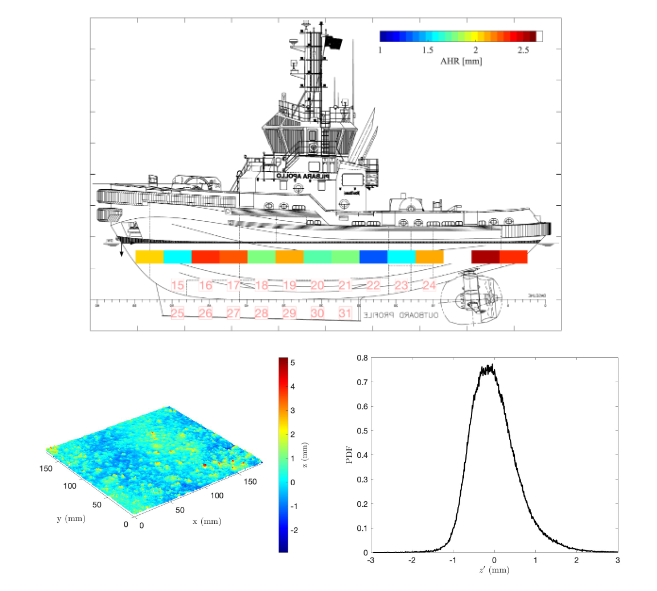
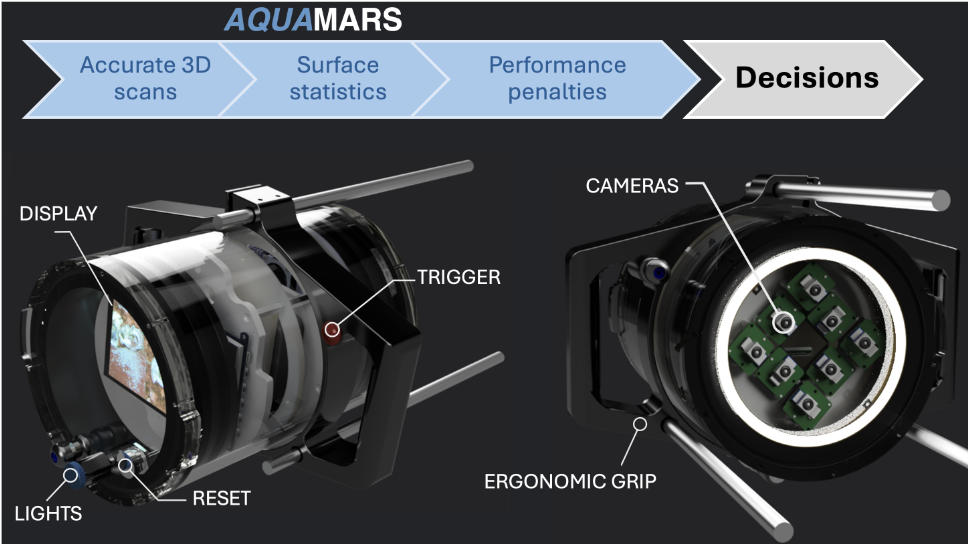
What This Calculator Does
This tool helps vessel operators estimate the economic and environmental impact of hull fouling based on actual research data from the University of Melbourne. It synthesizes findings from multiple studies, including measurements on the cruise ship and a tugboat.
Research-Based Tool
This calculator is built using direct measurements and validated outcomes from University of Melbourne studies using AQUAMARS (Advanced Quality Underwater Mapping and Analysis for Rough Surfaces) technology. The calculations represent real-world impacts measured through advanced 3D underwater scanning.
Simply:
- Select your vessel type
- Adjust operating costs if needed
- Set the hull fouling severity
The calculator will instantly show you:
- Additional fuel costs at different speeds
- Percentage increase in operating expenses
- Added CO₂ emissions from reduced efficiency
- Estimated annual impact on your operations
Source Research Papers
This calculator is based on the following University of Melbourne research studies. To access these papers and understand the methodology, measurements, and findings in detail, please click on the papers below:
As more research studies become available, this calculator will continue to be updated with additional vessel types and more refined friction coefficients for different fouling conditions.
Vessel Parameters
Cost Impact Analysis
Cost & Emissions vs. Speed
This chart shows how operating costs and emissions increase with speed for both clean and fouled hulls. The difference between the two cost lines represents your potential savings from hull maintenance.
Understanding The Model
The calculator uses a physics-based model that accounts for both frictional resistance (affected by fouling) and wave-making resistance (primarily affected by speed). The fouling impact values at FR4 (2.8mm roughness) are directly measured from University of Melbourne research, with intermediate values derived from fluid dynamics modeling.
Research Foundation
This calculator integrates findings from University of Melbourne marine engineering research, using advanced physics-based models to calculate drag and resistance.
Key Findings
- Heavy calcareous fouling increased friction coefficient by up to 193%
- For a medium-sized cruise ship, this translates to approximately $3M in additional annual fuel costs
- CO₂ emissions increase proportionally with fuel consumption
- The physics model accounts for both skin friction and wave-making resistance
Ongoing Research
This calculator will be updated as more University of Melbourne studies become available. Future enhancements will include additional vessel types, more refined friction coefficients for different fouling conditions, and the ability to calculate acoustic impacts of hull fouling.